Browse Items (42 total)
Sort by:
-
"After the Moon - What? Minutes of the Manned Flight Awareness Seminar."
The seminar was held at the Manned Spacecraft Center, September 25-26, 1969. -
"Application of the Saturn V Launch Vehicle to Unmanned Scientific Exploration of the Solar System."
According to the foreword, "This paper presents the results of a twelve-week mission and systems analysis of a combined Jupiter orbiter/solar probe mission utilizing the Saturn V launch vehicle." -
"Design, Development, and Fabrication of a Prototype Hydraulic Transformer."
For presentation to the Society of Automotive Engineers, 16 September 1964, Boston, Massachusetts. ABSTRACT: This paper discusses the design, development and fabrication of a prototype hydraulic transformer, Hydro-Aire Model No. 05-055, performed in fulfillment of the requirements of Contract No. NAS 8-5264 for NASA Marshall Space Flight Center. The Hydraulic Transformer described is designed to pump hydraulic oil at a flow of 100 GPM with a pressure rise of 4000 psi, and does this work by utilizing as a power source the flow of RP-1 rocket fuel at a pressure of 1900 psig. The Hydraulic Transformer built to handle this combination of flows and pressures, unprecedented in such devices, has a weight of only 70 pounds for the first development model. The development of this unit is discussed and future development improvements are mentioned. -
"Dynamic Problems in Launch Vehicles and Spacecraft."
Addresses improving spacecraft safety by resolving various known dynamic problems. -
"Engineering Safety Into Missile-Space Systems."
Safety Engineering, as applied to complex missile and space systems, has developed a new methodology referred to as "System Safety Engineering." The requirement for a comprehensive approach to safety which is included as a contractually covered adjunct to the design, development, and operational phases of a systems life cycle has become apparent from costly missile mishap experience. The general concepts and accomplishments of this new engineering discipline are described along with possible beneficial relationships with Reliability and other recognized organizational elements engaged in safety related activities. -
"High Energy Missions for Saturn."
Presented to Society of Automotive Engineers, Advanced Launch Vehicle & Propulsion Systems. When the Apollo lunar landing project is complete, the Saturn and Apollo hardware will only have begun to realize their ultimate potential for space exploration. The immense reserve of Apollo technology, facilities, and booster capability can then be directed to the achievement of national goals which lie far beyond the initial lunar landing. In achieving the Apollo lunar objectives, large investments will have been made in launch facilities, tracking systems, propulsion techniques, reentry systems, lunar landing systems and rendezvous technologies. Although developnent in these specialized areas has been tailored to the needs of Apollo, numerous studies by NASA and industry have demonstrated the feasibility of using the spacecraft, launch vehicles, and operating techniques for missions far more complex than lunar landings. Amortization of this hardware will prove cost-effective for missions of more sophisticated applications. -
"Interface Problems in Space Experimentation."
Space experimentation is expanding rapidly. Unmanned satellites are being equipped with precision instruments of greater power, and manned space stations accommodating large crews are in the drawing-board stage. The interface problems between these sophisticated instruments and between man, the spacecraft, and the supporting groundstations are multidimensional. This paper analyzes the scientific/technical areas of space experimentation, and continues with a review of the subsystems and support systems required to supply and operate the large variety of instruments. Areas of major integration efforts are singled out and the requirements for further developments and improvements are listed. A bibliography of 95 references is enclosed to assist in the identification of more detailed reports on all vital aspects of space experimentation.; Archive copy is a photocopy.; Supplement to IEEE Transactions on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, Vol. AES-2, No. 4, July, 1966. Pages 237 to 255. -
"Maintenance Data - How and What."
This presentation is concerned with how maintenance data can be collected, what can be done with it and possible a few arguments why it should be of any concern. -
"Materials in space exploration."
This paper presents a general review of major structural alloys that have been used in liquid rockets and space vehicles, the current state-of-the-art as applied to the Apollo launch vehicle systems, and discusses some materials currently under development for future requirements in vehicles for space exploration. Some aspects of the importance of corrosion resistant materials and suitable protective measures are discussed, as applied to both flight hardware and associated ground support equipment. -
"Meteoroid measurements with Project Pegasus."
Presentation at the Northeast Electronics Research and Engineering Meeting, Boston, Massachusetts, November 4, 1965. Ernest Stuhlinger, Director, Research Projects Laboratory, George C. Marshall Space Flight Center (NASA), Huntsville, Alabama.; INTRODUCTION: The prime objective of Project Pegasus is to measure, in the vicinity of the earth, the meteoroid penetration frequency in aluminum sheets of thicknesses which approach those of space capsule walls. Plans for the project were initiated at NASA in 1962 by the Office of Advanced Research and Technology and the George C. Marshall Space Flight Center. Throughout the project, members of the Langley Research Centers supported the project with experiments and advice. -
"MSFC specifications, standards and procedures microfiche reference file index."
This reference file has been prepared in order to identify data contained on microfiche in the MS-D Repository. This index is divided into three sections. Section I - MSFC Specifications, Section II - MSFC Standards, and Section III - MSFC Procedures. This listing will be kept up-to-date and will be published monthly.; Prepared by: RCA Service Company.; April 15, 1968.; Rpt. #005 (handwritten on the cover). -
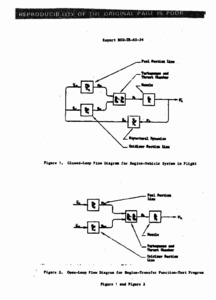
"Pogo analysis of the Saturn Propulsion System."
Report that contians images of graphs, photographs and diagrams. -
"Propulsion development problems associated with large liquid rockets."
NASA technical memorandum, Propulsion and Mechanism Branch. Propulsion and Vehicle Engineering Division, Research and Development Operations. -
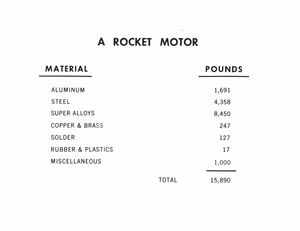
"Rocket motor" material list photograph.
8 x 10 inch black and white photograph of a rocket motor material list. The weight of the material is measured in pounds. -
"Saturn ascending phase guidance and control techniques."
Lunar Missions Meeting, July 17-19, 1962. Focuses on the guidence concept under development at the Marshall Space Flight Center -
"Saturn data summary handbook."
This handbook provides a technical data summary for the Douglas-produced Saturn S-IV and S-IVB stages of the NASA Apollo Program. Material contained in the S-IVB stage of this handbook includes the S-IB and S-V vehicles. This book will be updated as changes and additional information become available. The appendix contains aerospace fluid characteristics, LOX and LH2 vapor pressure curves and a list of non-standard abbreviations. -
"Selected methods for uprating Saturn vehicles."
This paper will discuss selected methods for increasing the Saturn launch vehicle payload capabilities. These methods involve system changes or additions that give large step performance'increases aver those which can be obtained by product improvements. The selected philosophy of approach and the established designed systems wil1,be described, as well as anticipatedsystem concepts that may be used to increase the Saturn vehicles' capabilities. -
"Sensitivity of rocket engine stability to propellant feed system dynamics."
Because of the increased reliability required of rocket systems in their more recently assigned missions, previously acceptable design features must be reappraised ad refined. In the region of rocket engine system stability, the probles is centered in two areas, the combustor and the propellant feed system The principal interest of this paper lies in the coupling that occurs between the feed system and combustion dynamics, often termed a "buzzing" instability then the dymics are characterized by periodic pressure oscillations in the range of 200 to 1000 cps appearing in the combustion chamber and' the feed system. -
"Signal distribution in automatic checkout systems."
This paper deals with several selected aspects of the signal distribution in automatic checkout systems. These are: 1) The use of relay matrices as control elements; 2) The inclusion of self-checking capabilities; 3) Problems of systems integration. These aspects are not unique to automatic checkout systems. However, due to the nature of automatic checkout systems as presently being designed around digital circuitry, they find either fuller or different applications than in other types of systems. Also, while they are on the surface somewhat disconnected in nature, they tend to interrelate during the implementation of an automatic checkout system. -
"Space flight : first draft."
Appears to be a rough dfraft with editorial comments and revision notes. Includes references to figures and tables.; Page 31 is missing. Pages 37 through 44 do not exist; there is a note about this on page 36. Page 67 also does not exist. -
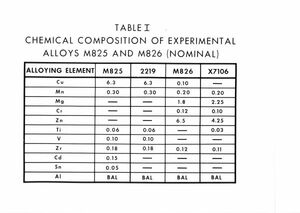
"Table I : chemical composition of experimental alloys."
8 x 10 inch black and white photograph of a table reperesenting the chemical composition of alloys M825 and M826. -
"Technical Information Summary Apollo 8 (AS-503) Apollo Saturn V Space Vehicle."
This document is prepared jointly by the Marshall Space Flight Center laboratories R-AERO-P, R-ASTR -S, and R-P&VE-VN . The document presents a brief and concise description of the AS-503 Apollo Saturn Space Vehicle. Where necessary, for clarification, additional related information has been included. It is not the intent of this document to completely define the Space Vehicle or its systems and subsystems in detail. The information presented herein, by text and sketches, describes launch preparation activities, launch facilities, and the space vehicle. This information permits the reader to follow the space vehicle sequence of events beginning a few hours prior to liftoff to its journey into space. -
"Technical information summary Apollo-10 (AS-505) Apollo Saturn V space vehicle."
The document presents a brief and concise description of the AS-505 Apollo Saturn Space Vehicle. Where necessary, for clarification, additional related information has been included. -
"Technical Information Summary Apollo-9 (AS-504) Apollo Saturn V Space Vehicle."
The document presents a brief and concise description of the Apollo 9 Saturn Space Vehicle. -
"Technician inspects an RL10 liquid hydrogen engine."
A technician inspects an RLlO liquid hydrogen rocket engine OD the assembly floor. of Pratt & Whitney Aircraft's Florida Research and Development Center. The 115,000-pound-thrust RLlO was designed and developed for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration's Saturn S-IV azld Centaur space vehicles. -
"Technique for reliability circuit design review in space electronics."
Design review is becoming a basic requirement during the design and development of military systems. The main purpose of the design review is to increase the system's inherent and operational reliability. The major portion of this paper is the result of reliability's effort to comply with Paragraph 3.6 of NPC 250-1 Reliability Program Provisions for Space Contractors. The design review to be discussed is a reliability circuit design review with emphasis placed on what should be reviewed and the review techniques employed. The basic circuit design review prerequisites, component parts and their ratings, are discussed at the beginning of this paper. The remainder deals with the organization and reviewing of circuits. The review items include worst-case circuit performance, component applications, failure mode analysis, noise rejection, electrical stress, and the determination of component temperatures. Many examples are included to illustrate how each item was accomplished. This paper is intended not only to give the reliability analyst cognizance of basic design problems and troublesome circuits, but also, to aid him in formulating a design review program. -
"The Development of Servovalves with Improved Reliability for Space Vehicles."
Considerations for improvement in the reliability of the Saturn engine gimbal servosystems are briefly covered. The Saturn I servovalves operate with increased electrical input power. The Saturn V vehicle stages will use mechanical feedback actuators with increased electrical input power, larger orifices and nozzle sizes, larger torque motor wire size, and greater spool driving forces. -
"The impact of manufacturing on design as related to accessibility."
The purpose of this paper is to emphasize the need for accessibility in the assembly and maintenance of spacecraft. This is especially pertinent because accessibility to subsystems for replacement, repair, and maintenance has proven to be one of the more costly phases of preflight preparation. The most successful programs in this day and age have been when the design and manufacturing engineers work side by side around a mockup where solutions to the problems can be visually seen and solved, keeping in mind the assembly as related to accessibility. Therefore, it will be shown that in order to overcome the difficulties, designers should adapt a hard, fast ground rule that each unit must be accessible and individually removable without disturbing the other units.; Aeronautic and Space Engineering and Manufacturing Meeting, Los Angeles, Calif. Oct. 7 - 11, 1968. -
"The Influence of Apollo/Saturn V Launch Operations on Lunar Site Selection: Case 330."
This paper presents some relationships between Apollo/Saturn V launch operations and multiple lunar landing sites, including the means by which site selection could facilitate launch operations. -
"The instrumentation of space vehicle in connection with the successful Saturn flight tests."
Presented on September 21, 1962, at the Eleventh Tagung Der Deutchen Raketen - Gesellschaft, Koblenz, West Germany. Instrumentation sf the Saturn space vehicle represents a considerable effort during the development phase, for proper design evaluatian of this new configuration, its propulsion system, and its structure and control characteristics, an unprecedented number of measurements are required to be carried onboard and to be recovered, These measurements are expected to work properly and to furnish the design engineer with information that is not available by ground testing, -
"The role of weighing in the development and firing of missile and spaceships."
Speech regarding the importance of developing and upgrading space ships and space technology. -
"Toftoy statement to Senate Investigation Committee": Development of the Nike system.
Narrative report of general H.N. Toftoy - Informal interview with Mr. Robert E. Dunne, Assistant Counsel of the Senate Permanent Investigating Subcommittee, in the presence of Mr. P. K. Schaeppi. -
"U.S. Aerospace Program: missions and projects as of January 1, 1966."
The document contains four charts labeled "Investigation", "Exploration", "Utilization", and "Control". Each chart is organized chronologically, contains drawings of U.S. Aerospace Program Projects, and incudes written descriptions of each project. -
Space Journal, vol. 1, no. 5, March-May 1959.
This issue includes a statement announcing Space Journal's termination of all connections with the U.S. military and with the Rocket City Astronomical Association. At the time, commander of the Army Ballistic Missile Agency (ABMA) at Redstone Arsenal Gen. John B. Medaris was concerned that the publishers and writers, all in the employ of ABMA, were using their government positions for personal gain through the magazine. Topics covered in the issue include the dangers and feasibility of space travel, designing buildings for life on the Moon, and the existence of life elsewhere in the universe. -
Artist's Conception of the RL10-powered Saturn S-IV Stage.
This artist's rendering of the RL10-powered Saturn S-IV stage is depicted as heading toward deep space after separation from the booster. The drawing is accompanied with a brief description of the Saturn S-IV. -
Oral History Interview With Allen Ware
Allen Ware is originally from Atlanta Georgia. He attended Auburn University where he studied Industrial Design . He moved to Huntsville, AL in 1983 to work for a company called "Essex." He worked there from 1983-1991. There, he produced a variety of things. First, he helped produce the Hubble Space Telescope mock-up and crew trainers. Then, he produced some other shuttle mock-ups. After leaving "Essex," he started to work at Boeing in Huntsville where he worked on the International Space Station. There, Ware was an internal and external packager configurator. He did that job for 15 years. He then transitioned to support the Delta IV launch vehicle out of Decatur. There, he did secondary structure design for Delta IV components. Ware is currently an Engineering manager of a Mechanical design team. He has about 15 engineers under him that do spacecraft, aircraft, and launch-vehicle design.Tags Oral History -
Oral History Interview With George Hamilton
George Hamilton has lived in Huntsville, Alabama all of his life, and his father was a Charter Marshall Member in Huntsville. When he was working, George's father was chosen as a "guinea pig" to go up in the Pregnant Guppy, which was a large, wide-bodied cargo aircraft. Because of George's father's career and interest with NASA, it made George interested in the career as well. George has a lot of family stories like this, which all have inspired him to take on his career that he has now. After high school, George went to The University of South Alabama in Mobile to study Marine Biology. Over the summer he had a change of heart, so he decided to transfer to Auburn University for Mechanical Engineering. After he finished up with his degree, he started working in small, manufacturing spare parts for missiles. After this career, he started to work at Avco Electronics in Huntsville where he worked at the plant on the design side. After this, Avco started looking for people to go overseas on the construction side of the house, so George went overseas with them. Then he came back, got married, and received his Phd in Biomedical Engineering at The University of Alabama in Birmingham.Tags Oral History