Browse Items (6320 total)
Sort by:
-
"Little known engineer is father of 'Moon-Bug' idea."
News article that details the creation and function of a lunar module or "moon bug" created by Wernher von Braun. -
Photograph of Willie Armstrong Hutchens.
On back: "Aunt Willie" -
Draft of "Building the Moon Rocket."
"Building the Moon Rocket" was presented at the National Machine Tool Builders Association Meeting, Doral Beach Hotel, Miami, Florida on November 3, 1965 by Dr. Mathias P.L. Siebel, the Deputy Director, Manufacturing Engineering Laboratory. There are handwritten notes throughout. -
"Management problems faced in making future manned space exploration decisions."
This paper presents in synoptic form, an analysis of the management problems being faced in making fuhlre manned spaceflight decisions. It is an attempt to view the manned space program in total perspective - its relationship to other scientific research, other national programs, the role of Congress, the President's role, industry's role, and then show their relative influence and impact on decisior, making for the Post-Apollo period. -
Cycling 460 Miles at 19 Miles an Hour
This is an article from an unknown magazine or newspaper which is authored by Frank Shorland and is about how me won the Cuca Cocoa Challenge Cup. -
"Facilities Engineering for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration."
Article makes references to a film. Centers around the idea that testing space vehicles extensively before launch is cost control. -
Memorandum to update the "Apollo/Saturn Logistics Support Requirements Plan."
This memorandum contains the pages to be changed in the logistics program for the Apollo/Saturn Project. The logistics plan includes the design, procuring, manufacturing, and production processes. This plan formalizes the program, improves logistic support, and implements management and action plans. -
Stuhlinger, Ernst, 1992
Families -
"Countdown to Liftoff".
This is an article from the Boeing Magazine. The Archive copy is a very poor photocopy and is difficult to read.; About the time the S-IC-1 booster is lifting the first Apollo/Saturn V from the launch pad on its maiden unmanned flight next year, a Boeing systems test crew will begin static testing the S-IC-4 at Devils Swamp, Mississippi (MTF). Starting with S-IC-4, all Saturn V first stage boosters will be captive fired at MTF. At present, S-IC firings are conducted by MSFC's test laboratory at Huntsville. The first flight stage, the S-IC-1, was placed in the static test stand on 24 January 1966 and completed its test program 25 Feb. It was removed from the stand March 14 and is undergoing post-firing checkout. it is due to be shipped this summer to KSC where it will be mated to the two upper stages of Saturn V, the IU and Dummy Apollo payload. The S-IC-2 went into the static stand on March 22 and is being tested during April The S-IC-3 also will be tested at Huntsville in 1966. The job of putting the world's largest and most powerful rocket together will be accomplished in the world's largest building, the 52-story vehicle assembly building. -
"A Bibliography of Wernher von Braun."
The document is designated for internal use only. -
Transcript of the World War I diary of Archie Duncan Shannon.
Archie Shannon was a farmer who served in Company G of the 1st Pioneer Infantry in World War I. Shannon was born in Limestone County, Alabama on November 19, 1891, and at the time of his draft registration on June 5, 1917, he lived in Ardmore, Tennessee. Shannon reported for military duty on September 18, 1917 and entered training at Camp Pike, Arkansas.
This diary covers Shannon's experiences in the U.S. Army from July 1, 1918 to July 7, 1919. He describes his journey to France and details everyday life as a soldier, especially the discomforts of life on the front in both the Marne and Verdun sectors. Shannon discusses bathing and sleeping arrangements, gas masks, air raids, and the terrible sights of war-torn France while repairing roads and burying dead soldiers. Shannon includes descriptions of his involvement in the Meuse-Argonne Offensive, noting the continuous shelling, gas attacks, and miserable weather conditions. He also describes his company's reaction to the Armistice, writing, "Many happy hearts in our company everyone seems to take life anew."
Shannon spent the rest of his World War I service in Belgium, Luxembourg, and Germany, and he returned to the United States on July 7, 1919. A list of soldier names and hometowns is recorded in the back of the diary. Shannon died on May 20, 1969 and is buried in Gatlin Cemetery in Ardmore, Alabama. -
World War I diary of Archie Duncan Shannon.
Archie Shannon was a farmer who served in Company G of the 1st Pioneer Infantry in World War I. Shannon was born in Limestone County, Alabama on November 19, 1891, and at the time of his draft registration on June 5, 1917, he lived in Ardmore, Tennessee. Shannon reported for military duty on September 18, 1917 and entered training at Camp Pike, Arkansas.
This diary covers Shannon's experiences in the U.S. Army from July 1, 1918 to July 7, 1919. He describes his journey to France and details everyday life as a soldier, especially the discomforts of life on the front in both the Marne and Verdun sectors. Shannon discusses bathing and sleeping arrangements, gas masks, air raids, and the terrible sights of war-torn France while repairing roads and burying dead soldiers. Shannon includes descriptions of his involvement in the Meuse-Argonne Offensive, noting the continuous shelling, gas attacks, and miserable weather conditions. He also describes his company's reaction to the Armistice, writing, "Many happy hearts in our company everyone seems to take life anew."
Shannon spent the rest of his World War I service in Belgium, Luxembourg, and Germany, and he returned to the United States on July 7, 1919. A list of soldier names and hometowns is recorded in the back of the diary. Shannon died on May 20, 1969 and is buried in Gatlin Cemetery in Ardmore, Alabama. -
"Saturn V semi-annual progress report July-December, 1966."
MA-001-00202H.; MPR-SAT V 66-3.; ABSTRACT: This Saturn V Semi-Annual Progress report describes progress and major achievements from July 1, 1966, through December 31, 1966, in the Saturn V Program. -
"Tilt-A-Whirl Parts Price List"
This pamphlet gives the prices for the Tilt-A-Whirl ride components. -
Letter to Colonel John C. Nickerson, Jr. from Harold Sedrel.
Sedrel writes on behalf of Nickerson's character, though "unacquainted with the details of this particular case." -
"Manufacturing welding control by E. R. Seay, Group Engineer, Lockheed-Georgia Company."
Paper given at the American Ordnance Association Welding Section Panel. Focuses on the process of welding and development programs. -
Down Street Station
Map location of Down Street Station -
Memorandum for Dr. Mueller from Robert C. Seamans.
This memorandum details changes or changes to be considered in Apollo-Saturn nomenclature. It also contains the matter of the Apollo and AAP missions designs and changes Seamans wishes to see. -
"Planning for strategic deterrence in the 1970s."
Article discussing money-resources and the budget. -
Extract document listing army members.
The document provides the members' ranks, names, ASNs, ARMs, ASRs, and organizations. -
Duty reassignment for Edwin D. Burwell Jr.
Major Edwin D. Burwell Jr. was assigned to move from the 1147th to the 1103rd Engineer Combat Group. -
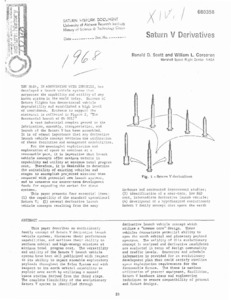
"Saturn V derivatives."
This paper desciibes an evolutionary family concept of !h turn V derivative launch vehicle systems, discusses their performance capabilities, and outlines their ability to perform orbital and hlgh-energy missions at minimum total program cost. -
"Highlights of General Electric's Participation in the U.S. Missile and Space Program."
Press release covering the system of functional management in NASA. -
Receipt of George W. Scott.
This receipt is from October 1, 1852 and notes Scott's wages and the price of wheat bushels. -
Letter from Charley Scott, Director of Instruction, to Christel McCanless, Librarian, at the University of Alabama Huntsville Center.
Scott notes his appreciation for McCanless' adept handling of the "Review of the Development of the Huntsville Campus Library." -
Statements by Charley Scott to the University of Alabama in Huntsville community.
This document is a text version of the statements Charley Scott made on May 16, 1964 on the education needs and challenges in Alabama. Scott notes that he is addressing "students, prospective students, parents, secondary school representatives, and members of the University of Alabama staff in Huntsville." He frequently quotes Dr. Frank A. Rose, President of the University of Alabama. -
ISCS International Solar Cycle Studies Scientific Committee on Solar-Terrestrial Physics 1998-2002 MAX IMPACT ISCS 2001 Workshop June 13-16, 2001 * Longmont, Colorado, USA.... Poster design courtesy of: UAH The University of Alabama in Huntsville
Poster Advertising the ISCS Worshop in Colorado in 2001. Poster features text and images of the Sun and Earth on a blue space-like background. -
Correspondence between William A. Schulze in Huntsville, Alabama, and Walter Dornberger in Buffalo, New York.
In his letter to Dornberger, Schulze congratulates him on his seventieth birthday and notes, "Looking back 29 years ago when I joined your organization in Kummersdorf, it is hard to single out specific important decisions you made and accomplishments achieved; to me they all appear of outstanding nature. I shall always be grateful for the friendship and experience gained in the development of rockets as a member of your team in those early years." Dornberger's reply is enclosed. -
Autobiography and résumé of William August Schulze.
In this partial autobiography, Schulze describes his experiences growing up in Neulaubusch, Germany and training and working as an engineer. He notes that he began working for Wernher von Braun at Kummersdorf in 1936 and then moved to Peenemünde, where he worked on the A-3, A-5, A-7, and V-3 rockets. The documents also include a lengthy handwritten excerpt from Schulze's 1945 day book and a résumé. Includes a transcription and a partial English translation. -
"Lunar Applications of a Spent S-IVB/IU stage (LASS)."
Support of lunar exploration missions is a major consideration in future space program planning. The spent Saturn v/S-IVB/IU can support both lunar - orbit and lunar -landing operations. This paper investigates lunar applications of the spent stage, and incorporates data generated during Company-funded studies. Investigated here is the feasibility of using a launch vehicle employing standard S-IC and S-I1 boost stages to deliver a modified S-IVB/IU and large discretionary payloads to a lunar orbit (LASSO) and/or the lunar surface (LASS). Operations in Earth orbit and direct-ascent trajectories are examined, and consideration is given to the use of the spent stage as a shelter in a manner similar to the presently planned Earth orbital workshop operations. Both the LASSO and LASS concepts are recommended for consideration in future lunar exploration plans. These concepts are capable of placing a gross wet weight of 101,400 lb in lunar orbit or landing 63,580 lb on the lunar surface respectively. The effective payload capability can be enhanced by proper integration of translunar mission subsystems with the subsystems required for lunar orbit or surface operations. The vehicles can be available within 3 years, with current-technology hardware sufficient for performing the missions described.; Douglas Paper No. 4256. -
"Digital Transducers."
This paper outlines the major advantages of digital transducers and describes the principles and features (1) direct digital transducers, (2) indirect digital transducers, (3) quasi-digital transducers, and (4) A to D transducers. -
"Automatic Pressure Transducer Calibration System."
The abstract notes, "The development of an automatic pressure transducer calibration system is discussed in this report. Evolution from past practices and systems into an automatic calibration system with computerized data handling is described." -
"The role of weighing in the development and firing of missile and spaceships."
Speech regarding the importance of developing and upgrading space ships and space technology. -
"Standard procedure for using units of mass, weight, force, pressure and acceleration."
Report No. DT-TM-1-60. ; FORWARD: The field of missiles and rockets deals with quantities of matter at various locations with different accelerations of gravity. The weight of these masses changes with gravity and the measurements of liftoff weight, fuel weight, etc., result in different values, depending on whether mass or weight units are used. Pressure and thrust are independent of the acceleration of gravity, but the instruments for measuring these values are calibrated with standard masses, producing different weight forces and calibration curves at different locations. Most sections of ABMA and other agencies or companies use pounds or kilograms as units of mass, weight or force, and the influences of different accelerations of gravity are often disregarded or treated incorrectly. These discrepancies become increasingly unacceptable with larger missiles and greater distances between operation sites. Therefore, the following Standard Procedure has been prepared to insure consistent and uniform terms and units of mass, weight, force, pressure and acceleration. All sections and individuals concerned are urged to use these units andprocedures. This is signed by Dr. Wernher von Braun, Director Development Operations Division. -
Letter to Robert K. Bell and Ray H. Jenkins from Major General Robert A. Schow, Assistant Chief of Staff, Intelligence.
Schow writes this letter in response to Bell and Jenkins request for classified information. Schow states that the convening authority will determine the relevance of the material before allowing access. -
Survey of Automatic Checkout Systems for Saturn V Stages.
The Abstract states "The four checkout systems developed and utilized by the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) for acceptance checkout of the Saturn V launch vehicle stages and instrument unit are described. The vehicle's characteristics, test policies, equipment design criteria, and operational factors are reviewed. Following a general description of each checkout system, this paper presents a brief definitive description of each major subsystem test station. These test systems are used for post-manufacturing and post-static firing acceptance checkout. The section related to the S-II stage includes several representative flow diagrams and descriptions of automatic tests. To present in detail the large volume of information describing these four checkout systems would require the writing of four papers." -
Loan contract between I. Schiffman and Thomas Wilson.
Loan contract for $225.00 for mules, horses, a cow, and equipment, borrowed by Thomas Wilson from Isaac Schiffman.