Browse Items (7888 total)
Sort by:
-
"Saturn IB inflight photographic instrumentation system."
This Internal Note presents the development of the Saturn inflight photographic instrumentation program from its original development requirement concept to the flight hardware application on Saturn vehicles. A comprehensive description of the infight photographic instrumentation system is given along with data concerning testing, operation, application, and evaluation of the system after recovery. This Internal Note shows that the system has been successfully developed,that valuable information has been obtained from film retrieved from recovered capsules, and that the system can be used with a high degree of reliability. -
"Saturn IB news reference."
Images, decriptions, graphics and explanations of the various Saturn rockets. -
"Saturn IB orientation training manuel."
Prepared through joint efforts of Personnel Department, Education and Development Branch, Systems Training Unit, Michoud Operations and Engineering Communications Department, Technical Information Branch, Applied Communications Engineering Section, Huntsville Operations.; This publication presents a brief descriptive summary of the Saturn IB vehicle and Chrysler's Corporation's accomplishments in the missiles and space field. The Saturn IB information presented herein is based on current plans for each of the stages. Although there may be design changes from vehicle to vehicle, the basic components, systems, and operating principles will remain similar to previous models. -
"Saturn IB SA-217 reference launch vehicle."
This document contains a definition of a reference Saturn IB launch vehicle designated SA-217. The Saturn IB SA-217 is a projected reference vehicle, based on Saturn IB SA-212, incorporating the latest proposed product improvements. The two-stage payload capability of this vehicle to a 100-nautical-mile circular orbit is 44,965 pounds. The Saturn IB SA-217 launch vehicle is to be used as the baseline vehicle for advanced studies requiring the use of the standard or modified Saturn IB launch vehicle. This vehicle definition does not necessarily represent approved changes to any specific vehicle. This document supersedes the Saturn IB SA-213 reference Launch Vehicle, described in memorandum R-P&VE-DIR-65-92. -
"Saturn IB/V Instrument Unit system description and component data: technical manual."
This manual contains a brief description of each Instrument Unit (IU) system and their respective components for S-IU-201 through 212 and S-IU-501 through 515. -
"Saturn IB/V instrument unit."
This brochure provides some basic, general information about the lnstrument Unit, a very important part of the Saturn IB and Saturn V launch vehicles. These launch vehicles are being developed primarily for the Apollo program for manned lunar exploration but will also be used for future space missions. -
"Saturn illustrated chronology : April 1957 - August 1963."
A list of images with detailed descriptions of what they are and their histories. -
"Saturn illustrated chronology : April 1957 - November 1962."
Document detailing the history of the saturn project between April, 1957 through November, 1962. -
"Saturn instrumentation systems."
Paper to be presented at the Third International Flight Test Instrumentation Symposium College of Aeronautics. A brief description of the Saturn vehicles is given, delineating the makeup of and differences between the Saturn I, Saturn IB, and Saturn V. -
"Saturn launch vehicle presentation."
Speech to be presented by C. L. Bradshaw, Deputy Director, Computation Division at Supervisor's Club, Knoxville Utilities Board. Speech praising the progress of space-based technologies and advancements. -
"Saturn launch vehicles : security classification guide."
This security classification guide is a compilation of previous individual classification assignments. Consideration of international affairs, the use and development of advanced technological information, and requirements of flight safety have influenced these assignments. -
"Saturn Radar Altimeter."
Paper given at the AIAA Guidance and Control Conference, August 12-14, 1963, Massachusetts Institute of Technology, Cambridge, Massachusetts. -
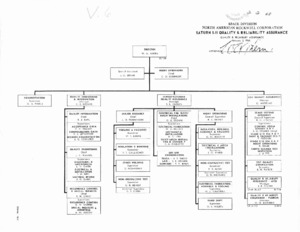
"Saturn S- II quality & reliability assurance : quality and reliability assurance" Organizational Chart.
Organizational Chart of the Rockwell Corperation, 1968 -
"Saturn S-IC annual progress report, 1964."
This report encompasses the progress made by The Boeing Company on the Saturn S-IC Program for the fiscal year 1964 (From July 1, 1963 through July 2, 1964). The main objective of this report is to serve as an historical presentation stressing Boeing accomplishments and present capabilities under Contract NAS8-5608. -
"Saturn S-IC annual progress report, 1965."
This Annual Progress Report has been prepared by the Boeing Company to fulfill the requirement under Article XXX, Paragraph A and C, Modification 100 of Contract, NAS8-5608 as amended by NASA letter I-MICH-DB, dated May 19, 1965, B. H. Aldridge to E. S. Olason. Subject: Change of NAS8-5608 to incorporate Quarterly Technical Progress into the Annual Progress Report. -
"Saturn S-IC booster : schematic."
This is page 7 of the Marshall Star : Space Information Digest. -
"Saturn S-II : annual progress report : 1 July 1962 through 30 June 1963."
This document, prepared in compliance with NASA contract NAS7-200, is the first annual progress report on the Saturn S-11 Program at the Space and Information Systems Division of North American Aviation, Inc. It provides a summary- and a technical analysis of results of contract work for the period 1 July 1962 through 30 June 1963.; SID 63-1028-1 251 pages. Include illustrations. -
"Saturn S-II annual progress report 1 July 1963 through 30 June 1964."
This document is the second annual progress report of the Saturn S-II Program. The report provides a summary and technical analysis of results of contract work by the Space and Information Systems Division of North American Aviation, Inc., for the period 1 July 1963 through 30 June 1964. This document was prepared in compliance with NASA contract NAS7-200. -
"Saturn S-II facilities organization."
Organizational chart for the Saturn II facilities. -
"Saturn S-II general manual."
This manual contains information covering the second stage of the Saturn V launch vehicle. -
"Saturn S-II ground support equipment inspection manual."
This publication has been prepared to provide preliminary inspection requirements and limitations on all ground support equipment to support the Saturn II stage of the Saturn V launch vehicle. -
"Saturn S-II stage program plan."
This documents outlines the S & ID plan to fulfill the requirements of Contracts NAS7-80 and NAS7-200 for the design, development and manufacture of the Saturn S-II stage.; APPROVED by R E. Greer, Vice President and S-II Program Manager.; This reissue supersedes all previous issues of this report.; FOREWORD: The S-II stage is 81.5 feet in length and 33 feet in diameter, with a usable propellant capacity of 970,000 pounds, The S-II propellants are fully cryogenic-liquid oxygen at -279 F and liquid hydrogen at -423 F. Its five-engine cluster provides one million pounds of thrust. The stage is a cylindrical structure of relatively light weight with a shell designed to resist all loads without the use of stiffening members. Its skin is of welded aluminum panels, as are the elliptical bulkheads of the fuel and oxidizer tanks. Unique to its design is the common bulkhead that separates the -423 F liquid hydrogen from the -247 F liquid oxygen. The common bulkhead - a sandwich of two 33-foot diameter aluminum domes separated by an insulating filler of honeycomb - eliminates the weight penalty that would be imposed by the second bulkhead in more conventional design. This document describes the S & ID program plan for development of the S-II stage and associated a support equipment. -
"Saturn S-IV cryogenic weigh system. Part I : propellant utilization."
In order to achieve maximum vehicle efficiency, it is essential that the vehicle propellants be loaded to desired values and that these propellants approach simultaneous depletion at the end of powered flight. To accomplish precise loading and assure minimum residuals, a highly accurate and repeatable, vehicle located, propellant management (PM) or propellant utilization (PU) system must be used. As the ability to load propellants to predetermined values depends directly on the ability of the system to accurately sense the propellant masses, it is essential that the system be calibrated with respect to propellant mass under conditions resembling those to be experienced during final loading and powered flight. The use of a cryogenic weight system will reduce the unknown factors in capacitance sensor element shaping, tank geometry, and propellant properties to a degree which will permit the determination of propellant masses to with .025%. -
"Saturn S-IV cryogenic weigh system. Part II : weigh operations."
Two basic methods for mass determination are: (1) direct measurement, (2) volume and density determination. Both methods or variations have been used to determine space vehicle propellant mass with varying degrees of success. Stringent propellant loading accuracy requirements of k0.5 percent for the Saturn S-IV Stage have led to the development of a Cryogenic Calibration Weigh System. The method employs accurate electronic force transducers and measuring systems as the standard and experimental weighings have verified achievement of better than the required accuracy. -
"Saturn S-IV cryogenic weigh system. Part IV : safety."
During cryogenic weigh system operation, hydrogen when combined with oxygen can create an unsafe condition. Therefore the concentration of the residual oxygen and hydrogen from leaks in the cryogenic weigh environmental bags must be known at all times during the cryogenic weigh. Hydrogen and oxygen detectors will provide the optimum method for maintaining safe conditions. Hydrogen properties and safe mixtures are reviewed. The method selected to analyze the oxygen content is discussed. The selection, development, and testing of a hydrogen detector system is examined. -
"Saturn S-IV engines."
Folder of information. -
"Saturn S-IV first firing."
Press release detailing the firing of the Saturn S-IV in California. -
"Saturn S-IVB quarterly technical progress report."
Douglas Aircraft Company Report DAC-56445, Saturn S-IVB Quarterly Technical Progress Report, covers design and development progress on the Saturn IB and Saturn V configurations of the S-IVB stage during August and September 1966. This report is prepared for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration under Contract NAS7-101. -
"Saturn S-IVB quarterly technical progress report."
Douglas Aircraft Company Report DAC-56533, Saturn S-IVB Quarterly Technical Progress Report, covers design and development progress on the Saturn IB and Saturn V configurations of the S-IVB stage during January, February, and March 1967. This report is prepared for the National Aeronautics and Space Administration under Contract NAS7-01.; Prepared for National Aeronautics and Space Administration under NASA contract NAS7-101.; Approved by A. P. O'Neal, Director, Saturn Development Engineering. -
"Saturn SA-1 flight and its instrumentation."
Presentation focusing on empahsising the importance of space programs such as Saturn. -
"Saturn ST-124-M inertial guidance platform."
a press release which focuses around the Apollo 9 flight and what role the ST-124-M inertial guidance platform has in it. -
"Saturn stages S-II : July 7, 1961 : Minutes of the phase II pre-proposal conference for stage S-II procurement."
Transcription of a confrence aiming to propose ideas for new rocket designs. Includes references to slides. -
"Saturn system study II."
Study regarding the three-stage carrier vehicle E-1 engines. -
"Saturn technical information handbook. Volume III of four volumes : SA-203."
The "Saturn Technical Information Handbook" provides up-to-date reference material to the Launch Operations Center personnel. This material shows the assembly and operation of the Saturn Vehicle components for systems analysis.; Volume II is available on the NASA Technical Reports Server (NTRS) as a PDF. -
"Saturn television system for SA-6."
The Saturn television system is an instrumentation device intended to provide visual information on vehicle performance in real time. The system covers the entire problem from the original image presented to the television camera to the presentation of the finished photographs for analyses. -
"Saturn V : non-stage procured launch vehicle ground support equipment."
The functions, authority, management relationships, and responsibilities of the Launch Vehicle Ground Support Equipment Project Office are described. Functions and examples of non-stage procured Launch Vehicle Ground Support Equipment (LVGSE) are described and illustrated. -
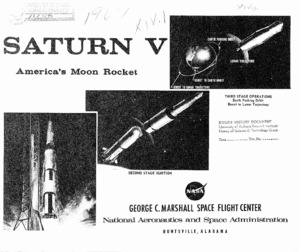
"Saturn V America's moon rocket."
Diagram that displays the Saturn V rocket with a page beneath detailing the function of each stage. -
"Saturn V Apollo Flight Configuration."
Drawn by Don Sprague at the Huntsville Engineering section of Boeing. -
"Saturn V Apollo flight configuration."
Diagram displaying the internal rooms, pieces and functions of the Saturn V as well as the space-suits of the astronauts. -
"Saturn V Apollo lunar orbit rendezvous mission."
Diagram explaining the process of a lunar mission from liftoff to recovery.