Browse Items (970 total)
Sort by:
-
"Sperry Rand monthly progress report for July, 1969."
The following pages contain reports for each of the individual contract appendices covering technical progress and accomplishments, related problems, and staffing progress. The report of manhours expended against each appendix by schedule order is being submitted as a part of the financial management report. -
"Stability analysis of Apollo - Saturn V propulsion and Structure feedback loop."
The propulsion and the structure of a space vehicle form a feedback loop through inertial coupling referred to as the pogo phenomenon and experienced with the Thor , Titan, and Apollo-Saturn V space vehicles. -
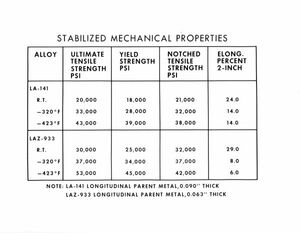
"Stabilized mechanical properties [table] photograph.
8 x 10 inch black and white photograph including a table that displays the stabilized mechanical properties of the following alloys: :LA-141 and LAX-933. -
"Standard procedure for using units of mass, weight, force, pressure and acceleration."
Report No. DT-TM-1-60. ; FORWARD: The field of missiles and rockets deals with quantities of matter at various locations with different accelerations of gravity. The weight of these masses changes with gravity and the measurements of liftoff weight, fuel weight, etc., result in different values, depending on whether mass or weight units are used. Pressure and thrust are independent of the acceleration of gravity, but the instruments for measuring these values are calibrated with standard masses, producing different weight forces and calibration curves at different locations. Most sections of ABMA and other agencies or companies use pounds or kilograms as units of mass, weight or force, and the influences of different accelerations of gravity are often disregarded or treated incorrectly. These discrepancies become increasingly unacceptable with larger missiles and greater distances between operation sites. Therefore, the following Standard Procedure has been prepared to insure consistent and uniform terms and units of mass, weight, force, pressure and acceleration. All sections and individuals concerned are urged to use these units andprocedures. This is signed by Dr. Wernher von Braun, Director Development Operations Division. -
"Standards of conduct for NASA employees."
NASA handbook which establishes what code of conduct is acceptable as a representative of the company and what behavior is not. -
"Statement of George E. Mueller, Associate Administrator for Manned Space Flight before the Committee on Aeronautical and Space Sciences, United States Senate."
Presentation of George Mueller before congress. Contains illustrations. -
"Statement of George E. Mueller, Associate Administrator for Manned Space Flight."
Volume I - Text. A statement given by George E. Mueller to the Committee of Aeronautical and Space Sciences. -
"Static test of Saturn V S-IC : news release.
Report after second Saturn V flight test. -
"Statistical model for Saturn electrical support equipment mission availability."
This report presents the logic leading to a mathematical expression for mission availability. Mission availability is treated as the probability that the cumulative downtime occurring during a mission of given length will be less than the time constraint. This is opposed to more general approaches such as steady state or instantaneous availability or operating time versus real time. We intend to present a practical and usable mathematical model by deduction and demonstration. The development is based on exponentially distributed downtimes. Experience shows that certain systems follow exponential downtime distributions except near zero. This error is often so small that it may be neglected. A future report will present a downtime distribution which will account for this small error. -
"Structural problems of large space boosters."
Report discussing the flaws in having large rocket boosters.