Browse Items (970 total)
Sort by:
-
"Saturn S-IV cryogenic weigh system. Part I : propellant utilization."
In order to achieve maximum vehicle efficiency, it is essential that the vehicle propellants be loaded to desired values and that these propellants approach simultaneous depletion at the end of powered flight. To accomplish precise loading and assure minimum residuals, a highly accurate and repeatable, vehicle located, propellant management (PM) or propellant utilization (PU) system must be used. As the ability to load propellants to predetermined values depends directly on the ability of the system to accurately sense the propellant masses, it is essential that the system be calibrated with respect to propellant mass under conditions resembling those to be experienced during final loading and powered flight. The use of a cryogenic weight system will reduce the unknown factors in capacitance sensor element shaping, tank geometry, and propellant properties to a degree which will permit the determination of propellant masses to with .025%. -
"Manned planetary flyby missions (based on Saturn/Apollo Systems) : executive summary report."
This report summarizes a study (by North American Aviation, Space Division) of Manned Interplanetary Flyby Missions to Venus and Mars during the period from 1975 to 1982. [The study was a broad but penetrating technical investigation of using a manned flight system for planetary exploration.] The results, along with previously known aspects of manned Mars and Venus flyby missions, vehicles, and systems, were integrated into total mission-system capable of performing a realistic and meaningful planetary exploration program. Manned Planetary Missions are feasible. Attractive multiplanet flyby missions can be performed by Saturn/Apollo systems. However, injected payload and mission requirements developed within the guidelines and assumptions of this study cannot be met with modified S-II or S-IV stages when used with the standard Saturn V Earth-launch vehicle. When using an Earth orbit assembly mode and an uprated Saturn Earth launch vehicle for application to manned planetary flyby missions, the launch vehicle should have a payload capability (2-stage to low Earth orbit) of 400,000 pounds or more for use with M(S)-IVB planetary injection stages. Manned planetary flyby missions provide a means of combining the favorable aspects of both manned and unmanned missions into a unique and highly effective planetary exploration mission-system capable of providing major significant inputs to the scientific and engineering questions concerning the interplanetary medium, our Sun, and our neighboring planets Venus and Mars. -
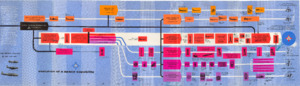
"Evolution of a Space Capability."
Two different organizational charts. -
"Manufacturing plan for Saturn S-II, Stages 16-25."
Manufacturing plan for for SII stages 16 through 25. -
"Organizational charts for Rocketdyne, a Division of North American Aviation, Inc."
Chart No. 1 Rocketdyne master approved by S. K. Hoffman, President (Vice President, North American Aviation, Inc.,).; Chart No. 6.1 Engineering Field Laboratories approved by R. J. Lodge, Director.; Chart No. 6.1.1 Santa Susana Field Laboratory, approved by D. M. Carpenter, Manager.; Chart No. 6.1.2 Field Laboratories Nevada Field Laboratory approved by G. J. Wunderlin, Manager.; Chart No. 6.1.3 Edwards Field Laboratory approved by F. F. Twight, Manager.; Chart No. 6.6 Engineering Administration approved by P. J. Kanne, manager.; Chart No. 12 Solid Rocket Division approved by T. E. Myers. -
"The Saturn S-II."
The S-II is the second stage of NASA's Apollo moon-landing rocket - the giant Saturn V. The most powerful hydrogen-fueled booster under production, the S-II is destined for Apollo manned lunar missions and will help power three Americans to the moon. The S-II is being developed and manufactured at Seal Beach, Calif., by North American's Space and Information Systems Division, Downey, Calif., under the technical direction of NASA's Marshall Space Flight Center, Huntsville, Ala. -
"Saturn S-II general manual."
This manual contains information covering the second stage of the Saturn V launch vehicle. -
"Welcome back planned for 'Gum Drop' crew."
A news article detailing the festivities planned upon the return of nine astronauts returning from a 10-day mission. -
"Dual ceremonies honor astronauts of Apollo 9."
A news article detailing the 'welcome back' ceremony for the nine astronauts who had just returned from a 10-day mission. -
"Company announces scholarship winners: Space Division places 9 of 21 boys and 16 girls."
A news article detailing the winners of scholarships from a competition held by Space Division. This contest was held for the children of Space Division employees.