Browse Items (970 total)
Sort by:
-
"Saturn IB - Saturn V instrument unit technical facts."
Press release detailing the technical aspects of the Saturn IB. -
"Saturn IB/V Instrument Unit system description and component data: technical manual."
This manual contains a brief description of each Instrument Unit (IU) system and their respective components for S-IU-201 through 212 and S-IU-501 through 515. -
IBM Apollo/Saturn Press information.
These are the facts about IBM's role as a NASA prime contractor in the Apollo/Saturn program. They are organized for quick reference. Computer terms are defined in a glossary. Glossy prints of photographs and illustrations are available from IBM information offices listed on the following page. Please order by photo number. Andrew J. Cella Manager of Information, IBM Federal Systems Division. -
"Instrument Unit in Crucial Test."
A three-foot high Instrument tional Business Machines Corporation will be launched into orbit with a huge Saturn second stage
later this month in a crucial test for the Apollo lunar program. -
"Fact Sheet : IBM Computer Will Direct Saturn Orbital Test Flight."
Press release regarding a IBM digital computer directing a Saturn 1B orbital mission. -
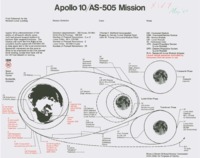
Apollo 10/AS-505 mission chart.
The chart includes diagrams, mission statistics, crew, and notes. There is an additional copy in the David Christensen Collection. -
"Sensitivity of rocket engine stability to propellant feed system dynamics."
Because of the increased reliability required of rocket systems in their more recently assigned missions, previously acceptable design features must be reappraised ad refined. In the region of rocket engine system stability, the probles is centered in two areas, the combustor and the propellant feed system The principal interest of this paper lies in the coupling that occurs between the feed system and combustion dynamics, often termed a "buzzing" instability then the dymics are characterized by periodic pressure oscillations in the range of 200 to 1000 cps appearing in the combustion chamber and' the feed system. -
"The reliability of the all-up concept."
Prepared for George C. Marshall Space Flight Center, Huntsville, Alabama under contract NAS8-11087. Publication No. 294-02-12-440. Special Technical Report No. 13.; INTRODUCTION: The Saturn/Apollo Systems Office at the George C. Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) requested ARINC Research Corporation to make a brief study of the reliability aspects of the All-Up concept. Under the requirements of Task 294-02 of Contract NAS8-11087, the study included a comparison between the reliability of the first Saturn V vehicle if All-Up, and its reliability with dummy upper stages. -
"Test procedure validation by computer simulation."
Digital computer simulation of the Saturn I Instrument Unit electrical networks was accomplished using the Discrete Network Simulation programs. The schematics were analyzed and a logic model prepared which consisted of a series of Boolean equations. The test procedures, which are written in the Acceptance, Test, or Launch Language (ATOLL), consist of a sequential set of computer instructions for the RCA llOA checkout computer to control the operation of the electrical networks. The procedures also contain the predicted results for each operation. The driving functions for the simulation of the model are generated from the ATOLL test tape by the Input Generator Program. The time sequenced operation of the networks is indicatedby the output from the simulation program in addition to the number of times each component in the system changes state. The results of the simulation are compared to the test procedure predictions on the ATOLL tape by the Comparator Program and any differences are listed. The Comparator Program also lists any component which did not change state at least once. -
"Organization of a countdown"
The Organization of a Countdown was developed over 8 years of missiles and space systems testing at the Douglas Aircraft Company, Sacramento test Center. The experience on which this study was based includes the Thor development and acceptance testing, Titan I second stage engine development testing, Development of liquid hydrogen handling techniques, Saturn S-IV and S-IVB development and acceptance testing. The intent of this paper is to examine the static test countdown organization and discuss the need for a systematic method to organize a countdown.