Browse Items (716 total)
Sort by:
-
"Techniques of implementing launch automation programs" (Saturn IB space vehicle system).
This paper identifies the methods and equipment through which automation is becoming a major factor in testing and launching Saturn IB space vehicles. The merits of a digital guidance computer and its impact in extending automated checkout are stressed; also a logical basis is established for computer and manual test control. Hardware and software elements of the automated system are described, and details pertaining to reliability are emphasized. A concluding appraisal suggests that automation will play an expanding role in future test and launch operations. -
Technical facilities and capabilities 1969.
This brochure is being distributed to colleges and universities to acquaint and interest their students, at all acadmic levels, with the wide variety of professional and technical skills that are essential to accomplish the complex mission of the Army Missile Command, located at Redstone Arsenal, enar Huntsville, Alabama. -
"Technical facilities & equipment digest."
This document portrays the capability of technical facilities and equipment at the George C, Marshall Space Flight Center (MSFC) , one of three basic field centers under the NASA Office of Manned Space Flight. -
"System safety handbook."
The testing of a hardware system consists of' subjecting it to carefully controlled operating conditions for the purpose of demonstrating that this system performs its function properly. -
"Saturn IB orientation training manuel."
Prepared through joint efforts of Personnel Department, Education and Development Branch, Systems Training Unit, Michoud Operations and Engineering Communications Department, Technical Information Branch, Applied Communications Engineering Section, Huntsville Operations.; This publication presents a brief descriptive summary of the Saturn IB vehicle and Chrysler's Corporation's accomplishments in the missiles and space field. The Saturn IB information presented herein is based on current plans for each of the stages. Although there may be design changes from vehicle to vehicle, the basic components, systems, and operating principles will remain similar to previous models. -
"System engineering propulsion, III-C-1."
Page numbering is inconsistent; there are no pages numbered 14 - 17. Some pages have handwritten numbers, others have no numbers at all.; The print quality of many pages is poor. Discusses the definition and function of propulsion as well as how to most effectively employ it . -
"System description for Saturn vehicle (SA-1 through SA-4)."
Missing pages iv, 3, 6 to 8. Photocopy of files containing sections of the project. -
"Systems applications in orbital launch operations."
The objective is to examine the technical requirements and feasibility of conducting orbital launch operations with systems now in the development phase. In order to maintain realistic constraints on the analysis, the Saturn S-IVB stage has been used as an example of present stage technology. The requirements, procedures and complexity of operations for orbital assembly and launch are discussed. The primary design requirement for orbital assembly and launch operations is increased orbital stay time (from hours to days or weeks). -
"A survey of propulsion problems as related to space vehicle design."
Incomplete document. Displays errors in space-vehicle design as they relate to space travel. -
"Survey of Saturn stage test and checkout computer program development."
This survey of the Saturn Stage Test and Checkout Computer Program Development contains a summary description of the systems developed for factory and static test of the stages of the SATURN IB and SATURN V Vehicles. The responsibilities of the MSFC and stage contractor organizations that are involved in test and checkout computer program development are briefly described. The test and checkout hardware and software (computer program) systems are given for each stage and for each site where tests are conducted. The systems and procedures that are used for program production verification, documentation, and change control required for the implementation of planned computer programs are included. Notes are included in the report to indicate what material is missing or incomplete. No attempt has been made to draw any conclusions regarding the automatic test and checkout systems being developed for each stage and the manner in which the efforts are organized, scheduled, and implemented. This document has been based on material provided by stage contractors and by components of MSFC through May 1, 1966. COMPUTER SYSTEMS SECTION. VEHICLE SYSTEMS INTEGRATION BRANCH. VEHICLE SYSTEMS CHECKOUT DIVISION.; SR-QUAL-66-3. -
"Propulsion and Vehicle Engineering Laboratory monthly progress report" May.
Monthly progress report for the Propulsion Division, May 1st through May 31st -
"Propulsion and Vehicle Engineering Laboratory monthly progress report" April.
Monthly progress report for the Propulsion Division, April 1st through April 31st -
"A summary of major NASA launchings" between October 1st and December 31st, 1968.
This is the first Quarterly Supplement to the October 1968 edition of GP 381, ''A Summary of Major NASA Launchings (Eastern Test Range and Western Test Range)." This Supplement covers the period from October 1 to December 31, 1968. Two additional Quarterly Supplements will be issued during 1969. Each of these will list those major NASA launchings occurring during the three-month period it covers. The basic publication will be revised and reissued, incorporating the information contained in the Supplements, as well as covering the final three-month period, subsequent to October 1, 1969. William A. Lockyer, Jr. -
"Structure of the NASA/Grumman lunar module."
Describes the structure and function of each part of the NASA Lunar Module -
"Structural problems of large space boosters."
Report discussing the flaws in having large rocket boosters. -
"Static test of Saturn V S-IC : news release.
Report after second Saturn V flight test. -
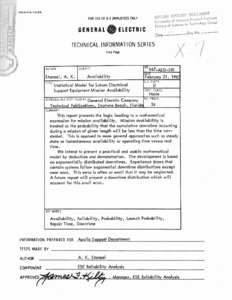
"Statistical model for Saturn electrical support equipment mission availability."
This report presents the logic leading to a mathematical expression for mission availability. Mission availability is treated as the probability that the cumulative downtime occurring during a mission of given length will be less than the time constraint. This is opposed to more general approaches such as steady state or instantaneous availability or operating time versus real time. We intend to present a practical and usable mathematical model by deduction and demonstration. The development is based on exponentially distributed downtimes. Experience shows that certain systems follow exponential downtime distributions except near zero. This error is often so small that it may be neglected. A future report will present a downtime distribution which will account for this small error. -
"Statement of George E. Mueller, Associate Administrator for Manned Space Flight."
Volume I - Text. A statement given by George E. Mueller to the Committee of Aeronautical and Space Sciences. -
"Statement of George E. Mueller, Associate Administrator for Manned Space Flight before the Committee on Aeronautical and Space Sciences, United States Senate."
Presentation of George Mueller before congress. Contains illustrations. -
"Standard procedure for using units of mass, weight, force, pressure and acceleration."
Report No. DT-TM-1-60. ; FORWARD: The field of missiles and rockets deals with quantities of matter at various locations with different accelerations of gravity. The weight of these masses changes with gravity and the measurements of liftoff weight, fuel weight, etc., result in different values, depending on whether mass or weight units are used. Pressure and thrust are independent of the acceleration of gravity, but the instruments for measuring these values are calibrated with standard masses, producing different weight forces and calibration curves at different locations. Most sections of ABMA and other agencies or companies use pounds or kilograms as units of mass, weight or force, and the influences of different accelerations of gravity are often disregarded or treated incorrectly. These discrepancies become increasingly unacceptable with larger missiles and greater distances between operation sites. Therefore, the following Standard Procedure has been prepared to insure consistent and uniform terms and units of mass, weight, force, pressure and acceleration. All sections and individuals concerned are urged to use these units andprocedures. This is signed by Dr. Wernher von Braun, Director Development Operations Division. -
"Standards of conduct for NASA employees."
NASA handbook which establishes what code of conduct is acceptable as a representative of the company and what behavior is not. -
"Stability analysis of Apollo - Saturn V propulsion and Structure feedback loop."
The propulsion and the structure of a space vehicle form a feedback loop through inertial coupling referred to as the pogo phenomenon and experienced with the Thor , Titan, and Apollo-Saturn V space vehicles. -
"A new telemetry technique."
A technique new to telemetry is discussed which promises to alleviate an enigma facing the telemetry engineer : How to adequately transmit the avalanche of vibration and other wideband data desired in the development phase of large missiles and launch vehicles. The data channels are stacked in the frequency spectrum as single sideband subcarriers which frequency modulate the RF carrier. The system design utilizes to advantage the statistical properties of vibration data to achieve maximum data transmission efficiency from the available RF carrier deviation. However, in contrast to proposed statistical predigestion techniques, the data is transmitted in raw form. -
"Sperry Rand monthly progress report for July, 1969."
The following pages contain reports for each of the individual contract appendices covering technical progress and accomplishments, related problems, and staffing progress. The report of manhours expended against each appendix by schedule order is being submitted as a part of the financial management report. -
"Space vehicle systems" research and technology.
A collection of various graphs, resumes and recordings for space vehical systems. -
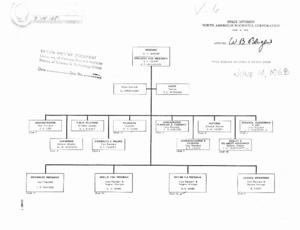
"Space Division, North American Rockwell Corporation Organizational Chart."
Organization chart for North American Rockwell, 1968 -
"Space vehicle test stands."
One of the pacing items in this Nation's accelerated space program is the construction of facilities for the manufacture, development, testing, check-out, transportation and launching of space vehicles. Behind each successful launching are countless hours of effort in development, quality and reliability checks and tests of engines, components, boosters, and stacked stages; including pressure tests, cold-flow tests and hot firing (or static) tests; all to assure the safest possible trip for the men or instrumentation in the space craft. -
Space vehicles for the peaceful exploration of the inner solar system; Memorandum to Mr. K. K. Dannenberg from Joe M. Jones.
Review of speech to be presented in Tampa, FL. Speech included references to slides. -
"Spacecraft television ground data handling system."
A design report which displays and explains how the Spacecraft Television Ground Handling System functions, is designed and what it might be used for in the future. -
"Space Station operations analysis using Gemini-Titan II-Agena."
Copy No. 026. Ger-10866. -
"Space sparks a renaissance in education."
An article which comments on the increasing interest in science and education due to the greater understanding of space. -
"Space flight projects - today and tomorrow."
NASA symposium on scientific and technical Information. -
"Space flight : first draft."
Appears to be a rough dfraft with editorial comments and revision notes. Includes references to figures and tables.; Page 31 is missing. Pages 37 through 44 do not exist; there is a note about this on page 36. Page 67 also does not exist. -
"Space and the working woman."
Memorandum prepared for the honoring Amelia Earhart by the Zonta Club, Birmingham, Alabama. -
Spaceflight: DDC report bibliography.
Bibliography containing space crews, space flights, satilites, cryogenic propellants, propaganda and the USSR. -
Space age vision [photograph].
8 x 10 inch black and white photograph. -
"Space age management or maintenance of technical capability during a period of retrenchment."
On January 3Ist of this year the United States celebrated its tenth anniversary in Space. In just one decade we have seen our space program climb from an humble beginning (a 30.8-pound payload put into orbit with a jury-rigged rocket) to extra-vehicular-activity and the tremendous Saturn V vehicle capable, of putting 250,000 pounds into low earth orbit. We have seen it grow from a "quick and dirty" operation to a program which at its peak had approximately 380,000 industrial employees in excess of {dollar}5.O billion per year. The marshalling of this great management and technological team generated many "growing pains". A few years ago the hue and cry was, "Where are we going to get sufficient people with scientific knowledge and drive to implement the space program?" Industry, sometimes reluctantly, was pressed into tasks which required managerial and technical skills beyond those they then possessed. -
Source credibility and personal influence in three contexts : a study of dyadic communication in a complex aerospace organization.
Abstract to "A thesis submitted to the faculty of Purdue University fo Gary Marshall Richetto in partial fulfillment of the requirements for the degree of Doctor of Philosophy, January 1969".; Handwritten note on front page: Return to Internal Communication, Room 223, 4202. -
"Some select physiological, anthropometric, and human engineering data useful in vehicle design and logistic problems of space flight operations."
Report No. DSP-TM-2-60 31 p.; Pages which were blank (not scanned): 2, 26, 28 -
"Some computer applications in Saturn stage checkout."
This paper discusses a number of interesting applications of digital computers in the checkout of individual Saturn stages and in the prelaunch checkout of the complete Saturn vehicle. It discusses the concepts of automation in Saturn checkout, the unique two-computer mode of operation at the launch site and the operations of the high speed data link connecting the two computers. Also discussed are the functions of the computer while propellants are loaded automatically on one of the stages; the functions of the display computer in the newest and largest Saturn display system, and operations and utilization of the Digital Events Evaluator, the main recording device utilized during stage checkout.