Browse Items (716 total)
Sort by:
-
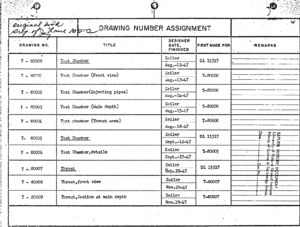
"Drawing number assignment"
The document is a photocopy of the Drawing Number Assignments from August 1947 to May 1953. Categories include but are not limited to the drawing number, title, designer, and date finished. Inscribed on the front is "original book property of Jay Laue, MSFC." -
"List of Academic Theses Since 1961 Related to the History of Aeronautics and Astronautics."
This preliminary listing of academic theses of interest to historians and social scientists is made available for general information, critical comments and related suggestions. The NASA Historical Advisory Committee suggested that such a listing might provide useful perspective on contemporary scholarship. Mr. Charles Atkins, a member of our Summer Seminar on "History, Social Science and Space" and graduate student in Political Science at M.I.T., kindly undertook this task. The NASA Historical Staff is also sponsoring preparation of a bibliography of bibliographies on the history of aeronautics and astronautics, and is undertaking a list of research resources available for academic scholarship. These will be available sometime this fall. Eugene M. Emme, NASA Historian.; NNH-61.; FOREWORD: This listing represents a first attempt to compile academic theses of relevance to the history of aeronautics and astronautics. It has been estimated that almost 70,000 doctoral dissertations have been completed in American universities since 1961, so this select compilation must be regarded as preliminary. In accord with the desire of the Historical Staff of the National Aeronautics and Space Administration to assist scholarly research, it is hoped that this list may be suggestive. It will, hopefully, stimulate a response which will permit additions to this listing of interest to historians and other scholars concerned with science, technology, and public policy in the twentieth century. -
"The development of a checkout language : ATOLL."
ATOLL was developed to fulfill the requirements for a common computer language that could be used by the test engineers for launch and factory checkout. "ATOLL" is the abbreviated name for Acceptance, Test, Or Launch Language. -
"Launch Vehicle Recovery System Requirements."
The primary considerations in the design and development of a recovery system applicable to present expendable first stage launch vehicles are discussed. The general requirements that define the essential characteristics of a feasible recovery system are derived from three critical phases during flight. The degree of criticalness is primarily influenced by the conditions at stage cutoff and separation. The three critical phses of flight are broken down into the following: (1) conditions and requirements between stage separation to re-entry; (2) re-entry; and (3) terminal descent and landing. -
"Failure Investigations of Large Liquid Propelled Rocket Engine Components."
Case histories of seven typical failures in large liquid propelled rocket engines components have been prepared. Quite simple to complex investigations are presented covering a variety of failure modes in a variety of materials. Included are successful solutions to the failure problems investigated.; Archive copy is a poor photocopy. -
"Operational Experiences on the Saturn V S-IVB stage."
This paper presents a light, but reverent, discussion of some of the Douglas operational experiences on the Saturn V/S-IVB stage. Certain relevant aspects of earlier work on the Thor intermediate range ballistic missile, the Saturn I S-IV stage, and the Uprated Saturn I S-IVB stage are also discussed.; Aeronautic and Space Engineering and Manufacturing Meeting, Los Angeles, Calif., Oct. 7 - 11, 1968. -
"History of MSFC Reliability Philosophy."
Paper given to North East Chapter , Mississippi Society of Professional Engineers. Essay discussing the history of the MSFC Reliability Philosophy. -
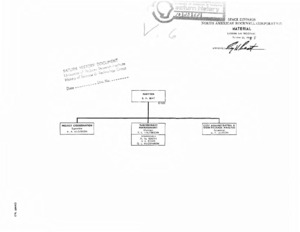
"Material : Saturn S-II program."
Saturn S-II Program Organizational chart. -
"Vibration and acoustic environment characteristics of the Saturn V launch vehicle."
This paper presents representative examples of vibration and acoustic data from flights of the Saturn V launch vehicle and static firings of Saturn V launch vehicle stages. The purpose of the paper is to provide vibration and acoustic environment characteristics which are pertinent to the design of launch vehicles -
"Recent NASA experience with hydrogen engines."
This paper presents a review of the experience which has accumulated in the development of the Liquid Hydrogen J-2 and RL10 rocket engines. These engines are being developed by the Rocketdyne Division of North American Aviation and Pratt & Whitney Aircraft, a Division of United Aircraft Corporation respectively.; On NASA Technical Reports Server (NTRS) as Unclassified; No Copyright; Unlimited; Publicly available. Also found on AIAA site.