Browse Items (175 total)
Sort by:
-
"S-IC Saturn booster."
8 x 10 inch black and white diagram of the Saturn booster engines. -
"S-II Engine."
8 x 10 inch black and white diagram of the Saturn II engines. -
"Saturn I : the first generation of heavy launch vehicles designed for peaceful exploration of space."
A basic description of the Saturn rockets alongside diagrams for context. -
"Saturn V specification index."
The purpose of the'saturn V Specification Index is to provide the official detailed record of all specifications and specification changes required for configuration management of the Saturn V Program and to report specification submittal and approval status. -
"Saturn V quarterly progress report : January - March."
Quarterly progress report for the months of January - March, 1966. -
"Saturn V specification cross reference index."
The purpose of the Saturn V Specification Cross Reference Index is to Supplement CM-004-001-2H, the Saturn V Specification Index. It is intended to provide a convenient means of finding the specifications by specification number which is cross referenced to Specification Matrix Number and contract end item number. More complete information on specifications including preparation, approval, and contractual status as well as all effective Specification Change Notices (SCN's) can be obtained from CM-004-001-2H, the Saturn V Specification Index which contains the master listing of the same specifications arranged in logical management and functional groupings and listed in Specification Matrix number order. More complete information on hardware can be obtained from various Saturn V Configuration Accounting Indices which list items by in contract end item (CEI) number order.; This document supplements the Saturn V specification index CM -004-001-2H of the same issued date. -
"Saturn V semi-annual progress report July - December, 1967."
This Saturn V Semi-Annual Progress Report describes progress and major achievements from July 1, 1967 in the Saturn V Program. -
"Saturn illustrated chronology : April 1957 - August 1963."
A list of images with detailed descriptions of what they are and their histories. -
"Saturn illustrated chronology : April 1957 - November 1962."
Document detailing the history of the saturn project between April, 1957 through November, 1962. -
"Saturn V : non-stage procured launch vehicle ground support equipment."
The functions, authority, management relationships, and responsibilities of the Launch Vehicle Ground Support Equipment Project Office are described. Functions and examples of non-stage procured Launch Vehicle Ground Support Equipment (LVGSE) are described and illustrated. -
"Memorandum for the administrator."
Very poor photocopy. Memorandum requesting additional information regarding a file attached to this one. -
"Minimax control of large launch boosters."
Keith D. Graham is principal mathematician, Systems and Research Center, Honeywell, Inc., 2345 Walnut Street, St. Paul, Minnesota.; Work done under NASA contract NAS 8-11206 from the George C. Marshall Space Flight Center.; ABSTRACT: A method of specifying the gains of a linear controller for a large launch booster using a new application of optimal control theory is described in this paper. Results for a specific example are included. An important control requirement is to maintain cost variables (such as bending moment, engine gimbal deflection, and lateral deviation from desired trajectory) within specified limits in the presence of load disturbances. This requirement is met by using a performance index which depends explicitly on maximum achievable values of the cost variables in a finite time interval. -
"Philosophy and practices of reliability as applied in the design of the Saturn Instrumentation System."
The basic engineering approach used in the Saturn instrumentation system has evolved to provide a highly reliable design for short periods of operation. The airborne measuring and telemetry systems including preflight tests, inspection, documentation, and feedback between the users and designers are discussed. The apparent differences between the practice and theory of reliability are rationalized. Some consideration is given to new problems in designing systems that must operate in hostile environments for long periods. The potential contribution of redundancy as a design concept is discussed.; This paper is concerned with the airborne measuring and telemetry systems; it does not attempt to treat the entire Saturn instrumentation system which consists of tracking devices including optical, radar, and Doppler, plus television, film cameras, and a myriad of instruments connected with factory checkout, ground test, and launch. -
"Development of the NASA/Grumman Lunar Module."
Paper regarding the actions and achievement of the Grumman Aerospace Corporation. -
"Nuclear engine design considerations."
The intent of this paper is to examine the static test countdown organization and discuss the need for a systematic method to organize a countdown. -
"Saturn and its mission."
Presentation from Harper, discussing the Saturn Project's then-status, background and plans. -
"SAA program specification - case 218."
Memo sent to Major General D. M. Jones - NASA/ML. -
"The instrumentation of space vehicle in connection with the successful Saturn flight tests."
Presented on September 21, 1962, at the Eleventh Tagung Der Deutchen Raketen - Gesellschaft, Koblenz, West Germany. Instrumentation sf the Saturn space vehicle represents a considerable effort during the development phase, for proper design evaluatian of this new configuration, its propulsion system, and its structure and control characteristics, an unprecedented number of measurements are required to be carried onboard and to be recovered, These measurements are expected to work properly and to furnish the design engineer with information that is not available by ground testing, -
"IU/S-IVB Forward Skirt Orbital and Translunar Thermal Analyses."
This report determines the maximum and minimum solar and terrestrial thermal energy incident and absorbed by Saturn IB/V vehicles in earth orbit and translunar travel. The influence' of this external energy on the Instrument Unit Thermal Conditioning System performance, and consequently its adequacy to maintain the electronic packages at acceptable temperature limits is ascertained. Conclusions are: a) Methanol/water coolant temperature will deviate from 111 specifications only during translunar cold flights. However, adequate thermal conditioning of the electronic equipment would still be maintained. b) Instrument Unit missions exceeding 6 1/2 hours, or electronic packages heat dissipation magnitudes lower than 3 kw or higher than 8.5 kw, should be reviewed to ascertain thermal compatibility. -
"Saturn V ground winds program."
The concept on Saturn V was to "budget" an amount for the dynamic portion of the wind load as a factor on the steady state drag. Wind tunnel tests paralleled the development and fabrication phases. The results indicated that the system was unable to withstand the design winds; thus, a decision was made to implement a viscous damper "fix" on the facility vehicle at the Kennedy Space Center. Damping tests in the Vertical Assembly Building (VAB) will have been completed and response tests on the pad will be in progress at the time of this symposium. This paper will present the history and status of this program to date. -
"Saturn V Apollo flight configuration."
Diagram displaying the internal rooms, pieces and functions of the Saturn V as well as the space-suits of the astronauts. -
"Crew Briefing : Instrument Unit Stage Presentation".
Document outlining different slides of a presentation containing numerous organizational charts, diagrams and bullet-list points. -
"Crew Briefing : Instrument Unit Stage Presentation".
Document outlining different slides of a presentation containing numerous organizational charts, diagrams and bullet-list points. -
"Instrument Unit Program Review : Saturn Instrument Unit."
Handwritten names and phone numbers on the first page. Apollo / Saturn Team. -
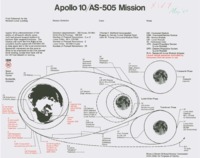
Apollo 10/AS-505 mission chart.
The chart includes diagrams, mission statistics, crew, and notes. There is an additional copy in the David Christensen Collection. -
"Organization of a countdown"
The Organization of a Countdown was developed over 8 years of missiles and space systems testing at the Douglas Aircraft Company, Sacramento test Center. The experience on which this study was based includes the Thor development and acceptance testing, Titan I second stage engine development testing, Development of liquid hydrogen handling techniques, Saturn S-IV and S-IVB development and acceptance testing. The intent of this paper is to examine the static test countdown organization and discuss the need for a systematic method to organize a countdown. -
"Apollo/Saturn consolidated instrumentation plan for AS-204/LM-1."
This report represents the consolidated instrumentation plan for employing optical and electronic data acquisition systems to monitor the performance and trajectory of the Apollo/Saturn 1B vehicle, AS-2 04/LM-1, during powered flight. Telemetry and electronic tracking equipment on board the vehicle, and data acquisition systems monitoring the flight are discussed. Flight safety instrumentation and vehicle data transmission are described, and geophysical information is provided. This plan reflects the general instrumentation coverage requirements set forth in the NASA Program Support Requirements Document (PSRD) for Apollo/Saturn 16, and the commitments of Eastern Test Range (ETR) Operations Directive (OD) No. 4206,dated 15 August 1967. This plan is not intended to conflict with or to supersede either document. The information presented in this document reflects planning concepts developed prior to October 1, 1967. -
The "Apollo/Saturn Data Handbook."
According to the preface, "This handbook provides KSC management personnel with general information relative to the Apollo-Saturn program. Emphasis is placed on Saturn launch facilities and related support equipment. Saturn vehicle parameters are included for general information. -
"Saturn V S-IC stage engine gimbal actuation system."
The actuation system for the Saturn V S-IC stage is described and compared to the Saturn I system. The use of mechanical feedback actuators that result in a significant increase in system reliability and the damping of load resonance is discussed. The unprecedented component sizes and system requirements are cited. -
"Saturn V S-IC stage engine gimbal actuation system."
The actuation system for the Saturn V S-IC stage is described and compared to the Saturn I system. The use of mechanical feedback actuators that result in a significant increase in system reliability and the damping of load resonance is discussed. The unprecedented component sizes and system requirements are cited. -
"Saturn I engine gimbal and thrust vector control systems."
The hydraulic systems for the two-stage block II Saturn I vehicle are described with the evolution of their development. -
DX priority: memorandum.
Memorandum discussing the priorization of various nlunar landing vehicle projects. -
"Plastics in space flight programs."
Article aimed at improving the NASA's ability to complete its projects." -
"Saturn V stage progress."
Report detailing the progress of the Saturn V's construction, focusing on the individual parts. -
"Part analysis program."
Includes carbon copy of letter sent to David L. Christensen from Ernst Lange regarding the Part Analysis program.